Tongue tie
Is also known as ankyloglossia, is a condition in which the thin membrane under the tongue (the lingual frenulum) is too short or tight, restricting the movement of the tongue. This can interfere with breastfeeding, speaking, and eating. It is a congenital condition, meaning that it is present at birth.
Causes of Tongue Tie
The exact cause of tongue tie is unknown, but it is thought to be a genetic condition that is passed down through families.
Symptoms may include:
- Difficulty breastfeeding, including poor latch and low milk intake
- Poor weight gain in infants
- Difficulty sticking out the tongue past the lower front teeth
- Difficulty making certain speech sounds, such as “l,” “r,” and “t”
- Difficulty moving the tongue from side to side or up and down
- Inability to play certain musical instruments, such as wind instruments
- Difficulty swallowing
- Protruding tongue
If left untreated, tongue tie can cause problems with oral hygiene, as well as difficulty with eating and speaking. It can also lead to problems with tooth alignment and jaw development.
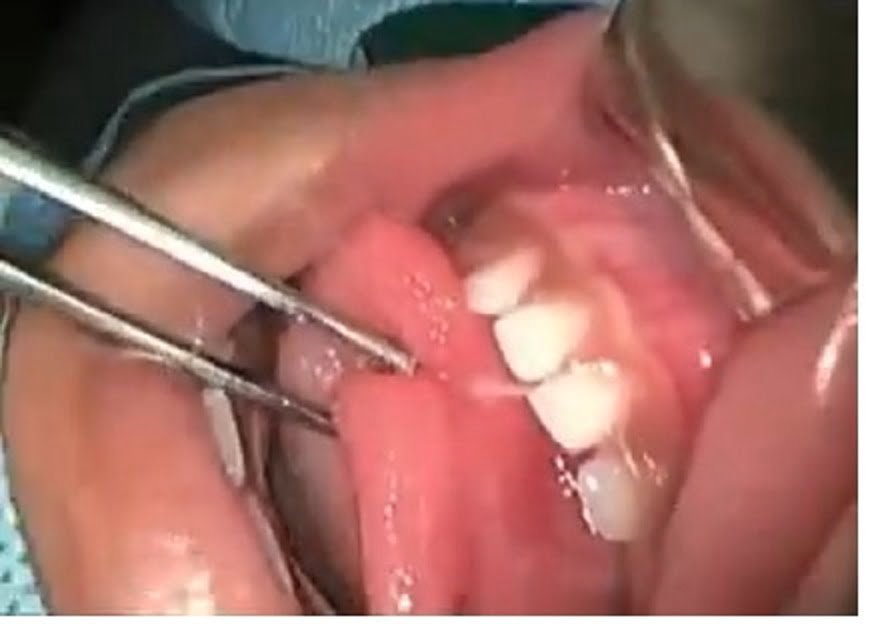
Treatment usually involves a simple procedure called a frenotomy, in which the lingual frenulum is snipped with scissors or a laser to release the tongue. Most babies and children recover quickly from the procedure, and there is usually little to no discomfort. Early treatment can help prevent future problems and improve quality of life.
Speech Therapy
In some cases, speech therapy may be recommended generally after surgery to help improve speech and language development in children with tongue tie. Speech therapy can help improve better articulation and clearer speech.

Recent Comments